calculate root size in bolt? Nicely, buckle up buttercup, as a result of this ain’t your grandma’s bolt measurement! We’re diving deep into the fascinating world of bolt root size, from the fundamental definitions to the complicated calculations. Think about attempting to assemble a spaceship with out figuring out the precise root size – chaos ensues! Get able to unlock the secrets and techniques of correct bolt measurements and turn out to be a bolt-length-measuring grasp.
Understanding bolt root size is vital in varied engineering functions, making certain structural integrity and security. This information gives an in depth clarification of the subject, protecting every little thing from totally different measurement strategies to the affect of assorted components on root size. We’ll discover the sensible functions of this data and equip you with the instruments and formulation it is advisable succeed.
Introduction to Bolt Root Size
Bolt root size is a vital dimension in fasteners, representing the space from the threaded portion of a bolt to the start of the shank. Understanding and precisely measuring this size is paramount in varied engineering functions, making certain the structural integrity and longevity of the assembled elements. Exact measurement ensures that the bolt is correctly engaged and might face up to the anticipated hundreds, avoiding potential failures.Correct measurement of bolt root size is essential for making certain the right functioning and security of bolted connections in constructions, equipment, and different functions.
This correct dimension is significant for stress calculations, fatigue evaluation, and making certain that the bolt can adequately transmit the required load. The appliance of right bolt root size calculations and applicable bolt choice instantly impacts the general reliability and sturdiness of the assembled elements.
Definition of Bolt Root Size
Bolt root size is the space from the top of the threads to the start of the shank of the bolt. This measurement is key in figuring out the bolt’s total energy and its suitability for the precise utility.
Significance of Correct Measurement
Exact measurement of bolt root size is crucial for a number of causes. It instantly impacts the load-carrying capability of the bolted joint, influences the fatigue lifetime of the connection, and is vital for making certain the structural integrity of the meeting. Inaccurate measurement can result in underestimation of stress and pressure, leading to potential failure of the bolted joint below load.
Widespread Models of Measurement
Bolt root size is usually measured in millimeters (mm) or inches (in). The selection of unit is determined by the precise utility and the system of measurement used within the design. For example, worldwide requirements usually make use of millimeters, whereas some older or localized requirements could use inches.
Comparability of Bolt Sorts and Typical Root Size Ranges
| Bolt Sort | Typical Root Size Vary (mm) | Typical Software |
|---|---|---|
| Coarse-threaded bolts | 5-20 mm (and above) | Normal-purpose functions, usually in heavy-duty equipment |
| Advantageous-threaded bolts | 3-15 mm (and above) | Functions requiring larger precision and load-carrying capability in tighter areas. |
| Excessive-strength bolts | Variable, usually 8-25 mm or extra | Vital functions demanding superior energy and resistance to fatigue, reminiscent of bridges and heavy tools. |
| Particular-purpose bolts (e.g., anchor bolts) | Variable, relying on the design | Used for securing heavy tools or elements to concrete or different supplies. Their size and dimension fluctuate broadly. |
This desk gives a basic overview of typical root size ranges for varied bolt sorts. Particular values could fluctuate relying on the producer, materials, and design specs. Consulting related engineering requirements and design manuals is essential for exact values in particular functions.
Strategies for Figuring out Bolt Root Size
Unveiling the exact root size of a bolt is essential for making certain structural integrity and stopping potential failures. Correct measurement strategies are important for engineers and technicians to design and manufacture dependable elements. This part explores varied methods for figuring out bolt root size, highlighting their respective strengths and limitations.
Direct Measurement Strategies
Direct measurement strategies present a tangible and readily verifiable strategy to find out bolt root size. These strategies contain bodily measuring the space from the seen bolt head to the foundation, using calibrated devices. This strategy is simple, but it calls for precision and cautious execution to keep away from errors.
- Caliper Measurements: Using precision calipers, the space between the bolt head and the foundation is instantly measured. This method requires the bolt to be in a secure place, minimizing any potential deformation or motion that would skew the measurement. Make sure the caliper’s jaws are accurately positioned to keep away from parallax errors, and double-check the readings for accuracy. Inaccurate readings can stem from poorly calibrated devices, improper positioning of the caliper, or operator error.
- Micrometer Measurements: A micrometer, identified for its excessive precision, gives a refined methodology for measuring bolt root size. The micrometer’s graduated scale gives detailed readings, enabling extremely correct measurements. A vital side is to make sure the micrometer’s anvil and spindle are correctly aligned with the bolt root to acquire an correct studying. Potential errors embody misalignment of the instrument and inconsistent utility of stress throughout measurement.
Oblique Measurement Strategies
Oblique measurement strategies depend on calculated values fairly than direct remark. These strategies are notably helpful when direct entry to the bolt root is restricted or difficult. These approaches require correct information of related parameters.
- Utilizing Drawings and Specs: Design blueprints and specs usually present dimensions for bolt root size. This methodology is environment friendly and available. Confirm the accuracy of the offered drawings in opposition to bodily samples. Inconsistencies between drawings and precise elements may result in inaccurate estimations.
- Utilizing Pc-Aided Design (CAD) Software program: CAD software program allows the exact dedication of bolt root size primarily based on the mannequin’s geometry. This methodology permits for a complete evaluation of the bolt’s dimensions. Guaranteeing the CAD mannequin precisely displays the bodily part is crucial. Discrepancies between the mannequin and the precise bolt can introduce errors in calculations.
Calculated Strategies
Calculated strategies leverage mathematical formulation to find out bolt root size, drawing upon identified parameters. These strategies provide a flexible strategy, however they rely on the accuracy of the enter knowledge.
- Making use of Geometric Formulation: Using geometric rules, the bolt root size might be calculated primarily based on identified dimensions of the bolt head and different related geometrical options. Exact measurements of the bolt’s dimensions are essential for correct calculations. Errors can come up from inaccurate measurements or inappropriate utility of the formulation.
- Utilizing Empirical Formulation: Empirical formulation present estimations primarily based on established relationships between variables, like head diameter and root diameter. These formulation provide a fast and dependable strategy. Nevertheless, the accuracy of the outcomes is determined by the applicability of the system to the precise bolt sort. Variations in bolt design can introduce errors within the estimations.
Accuracy and Precision Comparability
The accuracy and precision of measurement strategies fluctuate. Direct strategies, like utilizing calipers or micrometers, usually provide larger accuracy and precision resulting from their direct interplay with the bolt. Oblique strategies, whereas typically faster, would possibly introduce errors primarily based on the accuracy of the drawings or CAD fashions. Calculated strategies provide flexibility however are depending on the validity of the underlying formulation and the precision of enter knowledge.
It is essential to contemplate the context and utility when choosing probably the most applicable methodology.
Benefits and Disadvantages of Measurement Methods
| Measurement Method | Benefits | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Measurement (Caliper/Micrometer) | Excessive accuracy and precision; readily observable outcomes; tangible strategy | Requires direct entry to the bolt root; doubtlessly time-consuming for a number of bolts; liable to human error |
| Oblique Measurement (Drawings/CAD) | Environment friendly for a number of bolts; available knowledge; might be sooner than direct strategies | Reliance on correct drawings/CAD fashions; potential for errors if drawings are outdated or inaccurate; potential for misinterpretation |
| Calculated Strategies (Geometric/Empirical) | Versatile; doubtlessly sooner than different strategies; helpful when direct measurement is difficult | Reliance on correct enter knowledge; potential for errors in system utility; accuracy is determined by the validity of the system |
Components Affecting Bolt Root Size
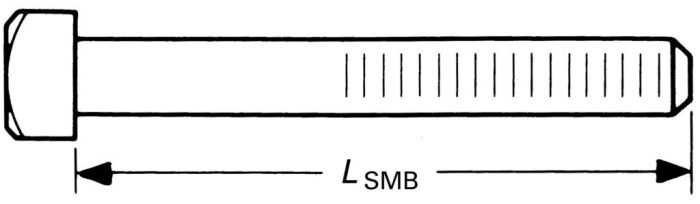
Bolt root size, a vital dimension in fastener design, just isn’t a hard and fast worth. Varied components intricately affect this parameter, affecting the general efficiency and reliability of the bolted joint. Understanding these components is paramount for reaching optimum design and stopping potential failures.Exact dedication of bolt root size is crucial for making certain the structural integrity and longevity of the bolted connection.
Cautious consideration of the influencing components ensures a strong and reliable meeting.
Materials Properties
Materials properties play a big function in figuring out the foundation size of a bolt. Totally different supplies exhibit various ranges of ductility, hardness, and tensile energy. These properties instantly affect the bolt’s capability to resist stress and deformation throughout set up and operation.
- Ductility: Excessive ductility supplies, like some stainless steels, can deform considerably with out fracturing, doubtlessly resulting in an extended root size in comparison with brittle supplies. It’s because the fabric can accommodate the deformation imposed throughout tightening. For example, a extremely ductile materials like annealed copper would possibly exhibit an extended root size than a hardened metal, even with equivalent design specs.
- Hardness: Tougher supplies, reminiscent of sure alloy steels, sometimes necessitate shorter root lengths to stop extreme deformation throughout tightening. The elevated resistance to deformation means the bolt is not going to deform as a lot, requiring much less root size to accommodate the load.
- Tensile Energy: Greater tensile energy supplies can face up to higher hundreds, usually suggesting the necessity for an extended root size to keep up the integrity of the joint. It’s because the fabric can bear a higher load with out failing.
Manufacturing Processes
The manufacturing course of employed considerably influences the foundation size. Variations within the manufacturing strategies can have an effect on the ultimate dimensions and traits of the bolt, together with the foundation size.
- Chilly Heading: Chilly heading processes, used for creating fasteners with particular shapes and dimensions, may end up in a particular root size. The method’s inherent constraints may end up in a predetermined root size that will not be ideally suited for all functions.
- Threading Strategies: The threading methodology used may affect the foundation size. Totally different threading methods have various results on the general geometry and dimensions of the bolt, doubtlessly influencing the foundation size. For example, a thread reduce utilizing a high-speed instrument could result in a special root size in comparison with a slower chopping methodology.
- Warmth Therapy: Warmth remedy processes can alter the fabric’s microstructure and mechanical properties, affecting the foundation size. These modifications can result in both a rise or lower within the root size, relying on the precise warmth remedy used. For example, a quenched and tempered metal bolt could have a special root size than a normalized metal bolt.
Design Specs
Design specs, together with the meant load, the kind of joint, and the working setting, play an important function in figuring out the suitable root size. These specs dictate the required energy and reliability of the bolted connection.
- Load Capability: The anticipated load on the bolt instantly influences the required root size. Greater hundreds usually require an extended root size to make sure adequate materials to soak up the stress and forestall failure. For example, a bolt meant for a high-pressure utility will seemingly have an extended root size than a bolt in a low-pressure utility.
- Joint Sort: The kind of joint (e.g., lap joint, butt joint) influences the stress distribution and the required root size. The geometry of the joint determines the stress focus factors and consequently impacts the foundation size requirement.
- Environmental Components: The working setting (e.g., temperature, corrosion) can affect the foundation size. Corrosion can result in materials degradation and require an extended root size to compensate for anticipated materials loss. For example, a bolt utilized in a corrosive setting will want an extended root size to account for materials loss.
Correlation Between Materials Properties and Bolt Root Size
| Materials | Typical Root Size Traits | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| Delicate Metal | Reasonable root size | Good steadiness of energy and ductility |
| Stainless Metal (304) | Barely longer root size | Greater ductility, good corrosion resistance |
| Alloy Metal (e.g., 4140) | Shorter root size | Greater hardness and energy, decrease ductility |
| Titanium | Variable root size relying on alloy | Excessive energy, good corrosion resistance, average ductility |
Calculating Bolt Root Size
Unlocking the exact measurement of bolt root size empowers engineers and producers to make sure structural integrity and optimum efficiency. Correct calculations are essential for designing elements that face up to anticipated hundreds and stresses, contributing to the reliability and security of the ultimate product. This part delves into the mathematical formulation and sensible functions for figuring out bolt root size.
Mathematical Formulation for Bolt Root Size
Understanding the mathematical foundation for calculating bolt root size is crucial. Bolt root size is usually decided primarily based on the precise design and utility. Whereas a common system could not exist, the calculations steadily depend on geometric rules and established business requirements.
Sensible Functions of Bolt Root Size Calculation
The sensible utility of bolt root size calculations extends throughout numerous engineering fields. From aerospace elements to automotive components, correct bolt root size is significant for making certain the integrity of the construction. By calculating bolt root size exactly, engineers can assure the bolt’s capability to resist anticipated hundreds, stopping potential failures.
Examples of Calculations for Varied Bolt Sorts and Dimensions
For example the applying of those formulation, let’s contemplate a number of examples.
- Instance 1: For the standard M12 bolt with a thread size of 30mm and a head diameter of 20mm, the foundation diameter is usually 11.5mm. The bolt root size is calculated by subtracting the pinnacle diameter from the full size of the bolt. On this case, assuming the full bolt size is 60mm, the foundation size could be 40mm.
- Instance 2: For a high-strength bolt utilized in a bridge assist, the design specs could embody an in depth drawing specifying the foundation diameter and the general size. In such a case, the foundation size might be instantly obtained from the drawing or the technical specs. The exact measurement is vital to make sure the bolt’s load-bearing capability aligns with the structural necessities.
- Instance 3: For a specialised bolt utilized in a stress vessel, the bolt root size could also be decided by contemplating the stress focus issue and the fabric properties of the bolt and the encircling elements. An in depth evaluation utilizing finite ingredient evaluation (FEA) could be vital for complicated designs.
Desk of Formulation and Functions
This desk summarizes the assorted strategies for calculating bolt root size, outlining their corresponding functions and formulation. The particular formulation and strategies used will rely on the precise bolt design and the engineering context.
| Bolt Sort | Method (if relevant) | Software |
|---|---|---|
| Customary Bolts (e.g., M12) | Root Size = Complete Size – Head Diameter | Normal-purpose functions, the place exact calculation just isn’t a main concern |
| Excessive-Energy Bolts | Derived from detailed design specs | Structural functions requiring excessive load-bearing capability, reminiscent of bridges and heavy equipment |
| Specialised Bolts (e.g., Strain Vessel Bolts) | Might contain FEA evaluation or stress focus components | Vital functions the place stress distribution and materials properties are paramount, like stress vessels and high-pressure methods |
Instruments and Tools for Measuring Bolt Root Size

Correct measurement of bolt root size is essential for making certain structural integrity and efficiency in varied functions. Exact measurement methods are important to ensure that the bolts meet the required specs and keep away from potential failures. Understanding the out there instruments and their capabilities is significant for reaching dependable outcomes.
Widespread Measuring Devices
Varied devices can be found for measuring bolt root size, every with particular benefits and limitations. Deciding on the suitable instrument is determined by the specified precision and the traits of the bolt. Familiarizing your self with these instruments empowers you to make knowledgeable choices about the best measurement approach in your wants.
- Calipers are versatile instruments for measuring exterior dimensions. Various kinds of calipers, reminiscent of digital calipers and vernier calipers, present various levels of precision. Digital calipers usually function computerized readings, enhancing effectivity and accuracy. Vernier calipers enable for exact measurements through the use of a sliding scale. Each sorts are broadly used resulting from their portability and affordability.
- Micrometers provide exceptionally excessive precision for measuring small dimensions. They’re notably priceless for exact measurements of bolt root size, the place minute variations can have vital penalties. Micrometers make use of a screw mechanism for exact motion and a calibrated scale for correct readings. They’re usually used for vital functions requiring superior accuracy, reminiscent of aerospace or high-precision manufacturing.
- Specialised Measuring Devices are designed for particular functions. These instruments could embody laser-based measuring units or specialised probes. Laser-based devices usually present extraordinarily correct measurements of distance and dimensions. Specialised probes are tailor-made for particular bolt sorts or functions, providing tailor-made options for numerous wants. These superior instruments could also be required for terribly tight tolerances or complicated geometries.
Options and Functionalities
Understanding the precise options of every instrument is crucial for choosing the suitable one for a given job.
- Calipers are characterised by their easy design and ease of use. They sometimes present measurements with a sure diploma of precision, usually adequate for a lot of general-purpose functions. Digital calipers present speedy digital readings, whereas vernier calipers require guide interpretation of the dimensions.
- Micrometers excel of their excessive precision. Their accuracy usually surpasses that of calipers, making them ideally suited for vital functions. The screw mechanism ensures exact motion and minimal error. They usually embody a ratchet cease for stopping over-tightening and potential injury to the half being measured.
- Specialised Measuring Devices usually function superior applied sciences, reminiscent of laser scanning or superior probe designs. These instruments could present real-time readings, automated knowledge assortment, and superior knowledge evaluation capabilities, contributing to elevated effectivity and reliability in measurements.
Calibration and Upkeep
Correct calibration and upkeep are essential for making certain the accuracy and reliability of measuring devices.
- Calibration entails evaluating the instrument’s readings to a identified commonplace. This ensures that the instrument precisely displays the precise dimensions. Common calibration is crucial for sustaining the instrument’s accuracy. Calibration schedules needs to be established primarily based on the instrument’s utilization frequency and required precision.
- Upkeep contains common cleansing and inspection. Sustaining the instrument’s cleanliness and performance prevents put on and tear. Correct upkeep ensures the instrument capabilities as anticipated and gives dependable outcomes.
Precision Ranges of Measuring Instruments
The next desk gives a comparative overview of various measuring instruments and their precision ranges. This data aids in choosing the suitable instrument for a particular utility.
| Measuring Instrument | Typical Precision Stage (in mm) |
|---|---|
| Digital Caliper | 0.01-0.05 mm |
| Vernier Caliper | 0.02-0.05 mm |
| Micrometer | 0.001-0.01 mm |
| Specialised Laser Measuring Units | 0.001 mm or much less |
Sensible Functions of Bolt Root Size Calculation: How To Calculate Root Size In Bolt
Correct calculation of bolt root size is paramount in making certain the structural integrity and longevity of bolted joints throughout varied industries. This exact measurement just isn’t merely a tutorial train; it is a cornerstone of security and effectivity, instantly impacting the efficiency and reliability of vital constructions. Understanding its sensible functions empowers engineers and technicians to make knowledgeable choices, minimizing dangers and maximizing the lifespan of their initiatives.Understanding the exact dimensions of a bolt root is essential for engineers and technicians.
This data ensures that the bolt can successfully face up to the meant load and prevents potential failure, making certain the security and reliability of the construction. A radical understanding of those calculations permits for optimized designs, minimizing materials waste and value overruns. This, in flip, contributes to a constructive affect on mission timelines and total success.
Actual-World Examples in Numerous Industries, calculate root size in bolt
Bolt root size calculation is significant in quite a few industries. Take into account the aerospace business, the place exact calculations are vital for plane structural integrity. A barely inaccurate bolt root size may result in catastrophic failure throughout flight. Equally, within the development business, bridges and high-rise buildings depend on correct bolt root lengths for stability and security. Improper calculation may compromise the structural integrity of those vital constructions.
Within the automotive business, exact bolt root size is crucial for engine meeting, chassis energy, and total automobile efficiency.
Impression of Inaccurate Measurements on Structural Integrity and Security
Inaccurate bolt root size measurements can have extreme penalties. A considerably shorter bolt root than specified may end up in untimely failure below load. This will result in expensive repairs, delays, and doubtlessly catastrophic penalties, particularly in high-risk functions like bridges and plane. Conversely, an excessively lengthy root can result in pointless materials waste and potential over-constraint points.
Significance of Correct Bolt Root Size in Engineering Functions
Correct bolt root size is crucial in making certain the environment friendly and dependable functioning of a wide range of engineering functions. In energy technology, correct bolt root lengths are important for the structural integrity of turbine elements. Failure to satisfy these necessities can result in expensive breakdowns and operational disruptions. Equally, in shipbuilding, exact bolt root calculations are important for the structural integrity of the vessel.
Insufficient bolt root size can compromise the vessel’s capability to resist the stresses of maritime operations.
Desk: Significance of Correct Bolt Root Size
| Trade | Significance of Correct Bolt Root Size |
|---|---|
| Aerospace | Vital for plane structural integrity, stopping catastrophic failure. |
| Building | Ensures the soundness and security of bridges and high-rise buildings. |
| Automotive | Important for engine meeting, chassis energy, and total automobile efficiency. |
| Energy Technology | Very important for turbine part integrity, stopping breakdowns and disruptions. |
| Shipbuilding | Essential for vessel structural integrity, making certain secure maritime operations. |
| Oil & Fuel | Important for making certain the security and reliability of pipelines and rigs. |
Troubleshooting and Error Evaluation
Exact bolt root size measurement is essential for structural integrity and efficiency. Understanding potential errors and easy methods to rectify them is crucial for sustaining accuracy and reaching dependable outcomes. This part gives a structured strategy to troubleshooting and error evaluation in bolt root size calculations.
Potential Errors in Measurement
Precisely measuring bolt root size requires meticulous consideration to element. A number of components can introduce errors, impacting the ultimate calculation. These errors can vary from easy human errors to extra complicated tools malfunctions.
- Inaccurate Studying of Measuring Devices: Careless or improper use of measuring instruments, reminiscent of calipers or micrometers, can result in inaccurate readings. Operator error, together with parallax errors (studying the dimensions from an incorrect angle) or improper instrument alignment, can considerably have an effect on the measurement. To mitigate these errors, guarantee correct instrument calibration and coaching for personnel utilizing the measuring instruments.
- Incorrect Bolt Identification: Utilizing the flawed bolt dimensions or figuring out the flawed bolt can result in misguided calculations. This can be a frequent mistake in meeting and manufacturing processes. Correct documentation and cautious identification procedures are important.
- Environmental Components: Temperature fluctuations and humidity can have an effect on the accuracy of measurements. Growth and contraction of the measuring instruments or the bolt itself resulting from temperature modifications may cause discrepancies. Utilizing temperature-compensated measuring instruments and controlling environmental situations throughout measurement are vital for decreasing such a error.
- Imperfect Floor Circumstances: Uneven or tough surfaces on the bolt head or the fabric it’s put in in could make exact measurements difficult. Utilizing specialised instruments or methods to compensate for floor irregularities is significant.
- Tools Malfunctions: Malfunctioning measuring instruments, reminiscent of calipers with broken jaws or worn-out micrometers, can produce inaccurate outcomes. Common calibration and upkeep of measuring tools are important.
Troubleshooting Methods
Addressing measurement errors successfully is essential for sustaining constant outcomes. This requires a proactive strategy to determine and rectify any points.
- Verification and Recalibration: Recurrently confirm the accuracy of measuring instruments utilizing calibrated requirements. Recalibration needs to be carried out in accordance with producer suggestions. This ensures that the measuring tools is in optimum situation.
- Double-Checking Measurements: Incorporate redundancy by having a number of operators measure the bolt root size independently. Evaluating outcomes helps determine discrepancies and potential errors.
- Environmental Management: Preserve a secure setting with constant temperature and humidity throughout measurements. This helps reduce errors associated to materials growth and contraction.
- Floor Preparation: Be certain that the surfaces of the bolt and the fabric it’s put in in are clear, clean, and freed from particles to allow correct measurements.
- Tools Upkeep: Adhere to producer pointers for sustaining and calibrating measuring tools. Common upkeep schedules and immediate repairs assist keep away from malfunctions and guarantee tools accuracy.
High quality Management Procedures
Sustaining accuracy in bolt root size measurements is significant for making certain the reliability and security of constructions. Sturdy high quality management procedures are indispensable.
- Standardized Procedures: Set up clear and concise procedures for measuring bolt root size. These procedures needs to be documented and adopted persistently by all personnel concerned.
- Calibration Protocols: Implement a strict calibration protocol for measuring devices to keep up their accuracy. This entails common calibration and documentation of the calibration course of.
- High quality Audits: Periodically conduct high quality audits to evaluate the effectiveness of measurement procedures and determine areas for enchancment.
- Error Monitoring: Set up a system to trace errors in bolt root size measurements, analyzing patterns and implementing corrective actions. This knowledge helps to grasp and forestall recurring errors.
Error Evaluation Abstract
This desk summarizes frequent errors and their options in bolt root size measurements.
| Error Class | Potential Error | Resolution |
|---|---|---|
| Instrument Points | Inaccurate studying, broken tools | Common calibration, correct use of devices, alternative of defective tools |
| Environmental Components | Temperature variations, humidity modifications | Preserve secure setting, use temperature-compensated devices |
| Materials Points | Tough surfaces, contaminants | Floor preparation, cleansing procedures |
| Operator Error | Incorrect identification, parallax errors | Correct coaching, double-checking, use of calibrated requirements |
| Course of Points | Insufficient documentation, inconsistent procedures | Standardized procedures, clear documentation, common audits |
Bolt Root Size and Design Concerns
Optimizing bolt root size is essential for making certain the longevity and structural integrity of mechanical methods. Correctly designed bolts with applicable root lengths can face up to the anticipated hundreds and stresses, minimizing the danger of failure and maximizing efficiency. This part explores the intricate relationship between bolt design and root size, highlighting the components that affect their interplay and the way contemplating root size improves total system design.
Affect of Bolt Design on Root Size
Bolt design considerably impacts the required root size. Totally different thread varieties, materials properties, and head types all contribute to the stress distribution across the root. A deeper understanding of those components permits for extra knowledgeable design selections. For instance, a bolt with a high-strength materials will seemingly require a special root size than one made from a lower-strength materials to realize the identical stage of security.
Equally, the kind of thread (e.g., coarse or superb) and head model have an effect on the stress focus on the root, impacting the required root size.
Components Influencing Bolt Root Size Design
A number of vital components should be thought-about when figuring out the optimum root size for a given utility. Cautious consideration of those components ensures the bolt can safely bear the anticipated hundreds.
- Materials Properties: The fabric’s tensile energy, yield energy, and fatigue energy are basic. Bolts made from higher-strength supplies can usually tolerate shorter root lengths for a similar load capability in comparison with lower-strength supplies. That is as a result of materials’s inherent capability to withstand deformation.
- Load Traits: The magnitude and kind of load (static, dynamic, or cyclic) the bolt will expertise considerably affect the required root size. Dynamic or cyclic hundreds usually necessitate longer root lengths to accommodate potential fatigue failures. Understanding the load spectrum is significant.
- Thread Kind and Pitch: The thread type and pitch have an effect on stress focus on the root. Advantageous-threaded bolts sometimes exhibit larger stress concentrations than coarse-threaded bolts, resulting in the necessity for longer root lengths.
- Bolt Diameter: Bigger diameter bolts sometimes require longer root lengths to keep up the identical security issue in comparison with smaller bolts below equivalent load situations. This can be a results of the elevated space for stress focus on the root.
- Preload: Preload, the preliminary tightening power utilized to the bolt, impacts the stress distribution and is instantly correlated with the bolt’s root size necessities. Greater preload usually permits for shorter root lengths whereas nonetheless sustaining sufficient security.
Significance of Root Size in Total System Design
Contemplating bolt root size through the preliminary design part is significant for the general efficiency and reliability of the mechanical system. A accurately calculated root size ensures the bolt can successfully transmit the meant load with out failure, thus stopping potential system injury and downtime. A poorly designed bolt, resulting from insufficient root size, can result in catastrophic failure, requiring expensive repairs or replacements.
Correctly accounted-for root lengths end in extra strong and sturdy methods.
Bolt Design Specs and Root Size Necessities
The desk beneath gives a comparative evaluation of assorted bolt design specs and their corresponding root size necessities. These values are illustrative and needs to be used as a information solely, with exact calculations tailor-made to the precise utility.
| Bolt Design Specification | Materials (e.g., Grade 8 Metal) | Nominal Diameter (mm) | Anticipated Load (kN) | Estimated Root Size (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Excessive-Energy Bolt with Heavy Preload | Grade 8 Metal | 12 | 50 | 20 |
| Medium-Energy Bolt with Reasonable Preload | Grade 5 Metal | 10 | 30 | 25 |
| Advantageous-threaded Bolt with Cyclic Loading | Grade 10 Metal | 8 | 20 | 30 |
Final Phrase
So, there you will have it – a complete exploration of bolt root size calculation! From defining the idea to sensible functions, we have coated all of it. Now, armed with this data, you may confidently sort out any bolt measurement problem. Keep in mind, correct measurements are key to profitable initiatives, and this information will make it easier to obtain simply that. Comfortable measuring!
Important FAQs
What are the frequent models used to measure bolt root size?
Widespread models embody millimeters (mm), inches (in), and centimeters (cm), relying on the applying and business requirements.
What are some frequent errors in measuring bolt root size?
Widespread errors embody utilizing the flawed measuring instruments, improper calibration, parallax error when studying measurements, and never accounting for the precise bolt sort and materials.
How can I enhance the accuracy of my bolt root size calculations?
Use high-precision measuring instruments, double-check your measurements, and thoroughly contemplate the components affecting root size, reminiscent of materials properties and manufacturing processes. Slightly additional care goes a great distance.
What are the potential penalties of inaccurate bolt root size measurements?
Inaccurate measurements can result in structural failure, security hazards, and expensive repairs. It isn’t definitely worth the danger; precision is paramount.
